Products
Solvers
Learning Center
Application Gallery
Knowledge Base
Support
License Agreement
Release Notes
Update and New
English
中文
Contact Number
+86-13776637985
Email
info@simworks.net
 Enterprise WeChat
Enterprise WeChat WeChat Service Account
WeChat Service Account
This section describes settings for dipole sources.
In FDTD, an electric dipole generates a field around the oscillating point charge, while a magnetic dipole exhibits field distribution around a current loop.
Select Dipole in the solver tab and create a dipole in the Composite viewer, then set further parameters in the Edit properties interface that automatically pops up.
In FDTD, a Dipole acts as source for generating the electromagnetic field in Maxwell's equations.
Typical electric and magnetic dipoles are shown in the figure below:
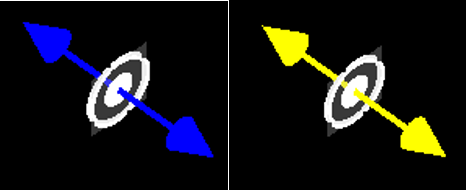
The Monopole, Dipole, Quadrupole, Hexapole, and Octupole can't be accomplished by a simple superposition of dipoles because polarization intensity, in this case, involves a complex polarization tensor that cannot be described by a superposition of dipoles.
General tab can be used to set properties of a dipole, such as phase shift and rotation. See general settings in Source.
Dipole option allows users to select the desired type of dipole.
| Name | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| Electric | Electric dipole. |
| Magnetic | Magnetic dipole. |
Gemetry tab can be used to set geometric dimensions of a source. See geometry settings in Source.
Wavelength/Frequency tab can be used to set wavelength/frequency of a source. See wavelength/frequency domain settings in Source.
In this case, a randomly excited Dipole source is used to calculate the bandgap of a photonic crystal. For details, see Bandstructure of 3D Cubic Lattice.