Contact Number
Email
 Enterprise WeChat
Enterprise WeChat WeChat Service Account
WeChat Service Account
 Wechat Channels
Wechat ChannelsThis section describes data visualization in the software.
Data visualization refers to selecting, plotting, and saving data in the Data visualizer window.
Data visualization enables direct display of complicated high-dimensional data and coordinate systems, allowing you to retrieve, view and display the data effectively.
Open the Data Visualizer window through corresponding interface operations. This window integrates a number of plotting methods and a dataset list of selected objects, allowing you to visualize data easily.
Right-click the object whose data you want to view in the Objects Tree, then click the Data Visualizer in the context menu to open the Data Visualizer window.
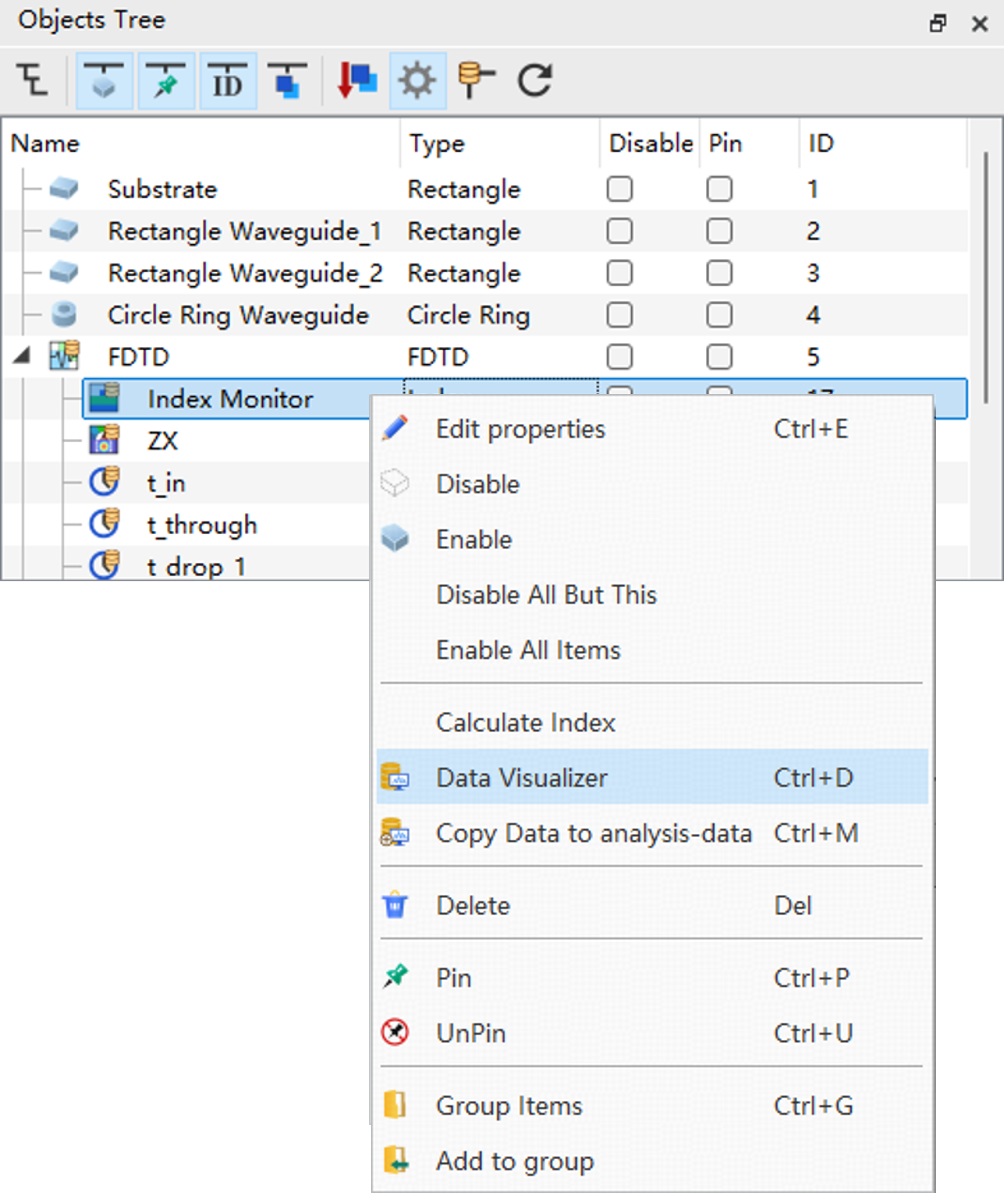
Within the Objects Tree, select the object whose data you want to view, and click the Watch Results Outline at the top of the screen. The Watch window will appear below the Objects Tree window, which displays the dataset list of the selected object. Right-click the desired data, and click the Visualizer in the pop-up menu to open the Data Visualizer window.
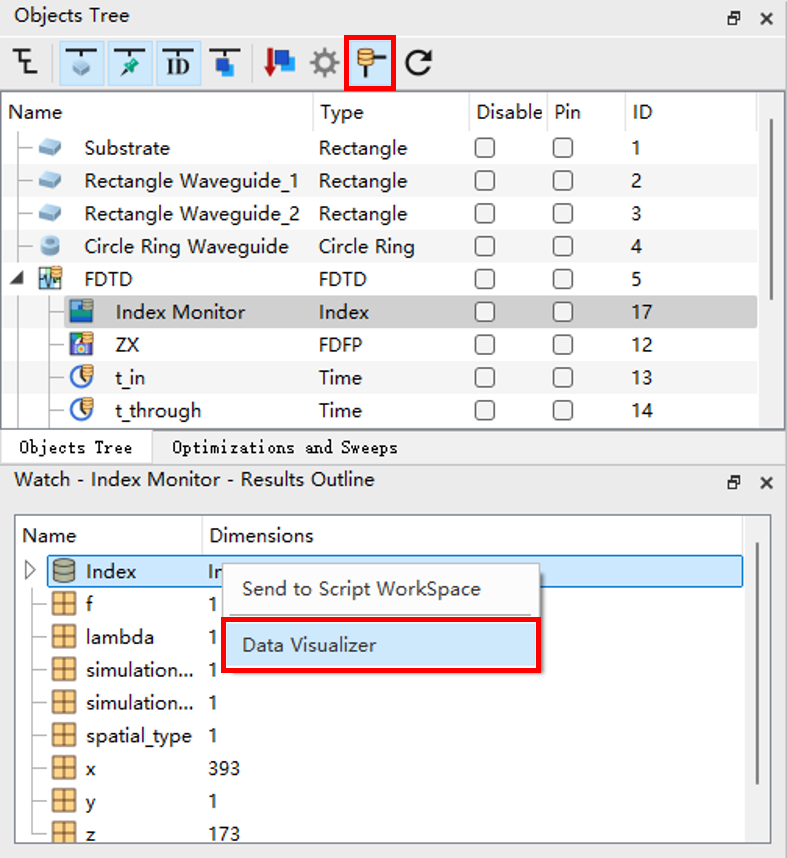
For the object in the Object Tree whose data you want to view, click the Watch results outline above the object tree window to switch the Watch to a dataset list. Right click on the object and click Data Visualizer in the context menu to open the Data Visualizer window.
In the Script Workspace window, right-click the data you want to view, then click the Visualizer Data in the pop-up menu to open the Data Visualizer window.

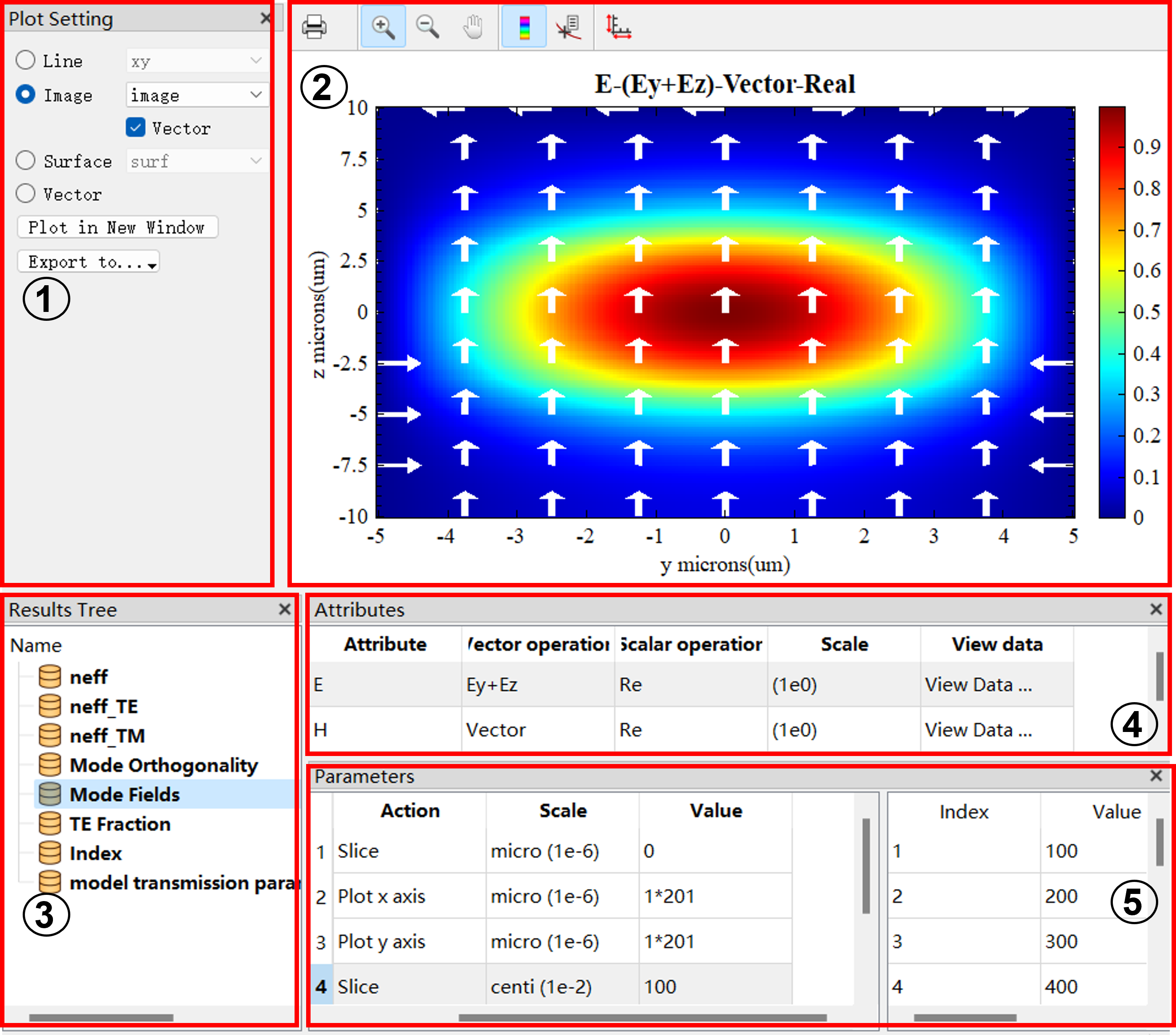
| Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Plot setting | Specify a type of plot and export it. |
| 2 | Plot | The image window. |
| 3 | Results tree | Select a dataset for plotting. |
| 4 | Attributes | Select vector components, real part, imaginary part, etc. |
| 5 | Parameters | Select plotting parameters. |
Plot setting:
Generally, the plot type will be automatically selected based on the dimensions of data. For example, when you have a one-dimensional dataset, the plot type chosen by the software is typically a 1D line plot. If you have a two-dimensional dataset, the software will automatically select a 2D planar graph as the plot type. For datasets with three or more dimensions, the software may automatically "slice" the data into a two-dimensional dataset, and display it in the Image mode. You need to select the "Image>Vector" to generate 2D vector arrow plots, or select the "Vector" to create 3D vector arrow plots.
Note: It's important to note that although the surf function is commonly used for plotting spatial surfaces, the underlying data is still two-dimensional.
Attributes
The attributes of the data can be determined by:
The software offers a variety of visualization methods, including:
| Name | Description | Figure | More |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plot | 1D line plot | 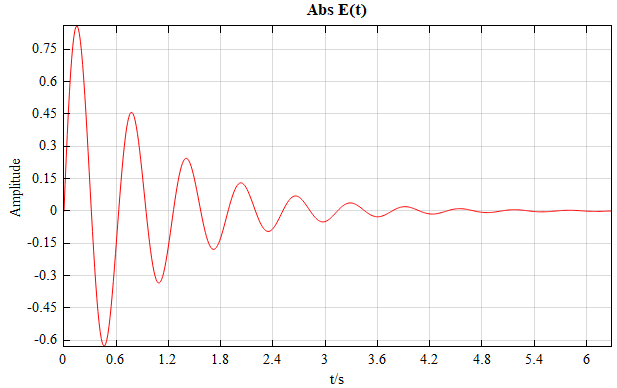 Take logarithm: Take logarithm: 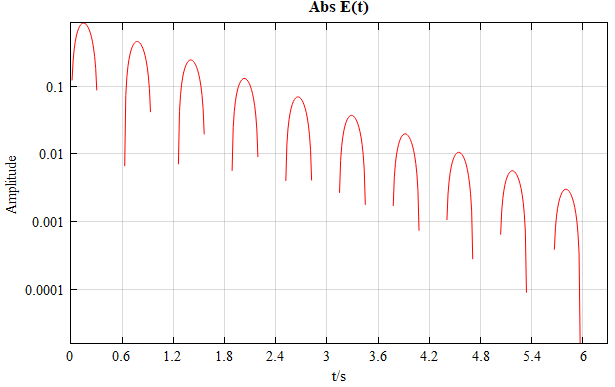 |
Line plot |
| Plotyy | 1D dual y-axis chart | 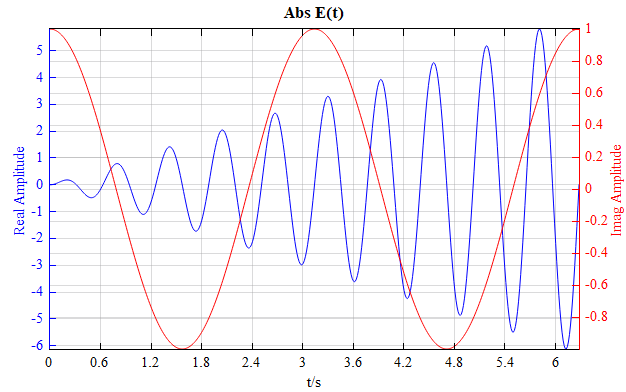 |
Dual line plot |
| Polar | 1D polar plot | 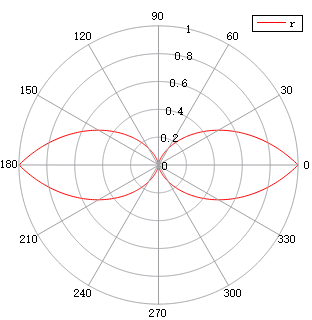 Take logarithm (pay attention to adjusting the range of the radial axis): Take logarithm (pay attention to adjusting the range of the radial axis): 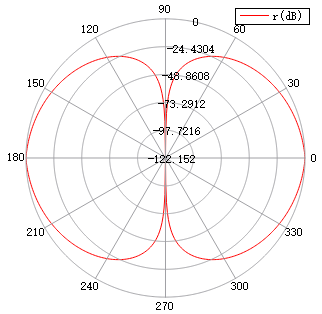 |
Polar plot |
| Smith chart | Smith chart | 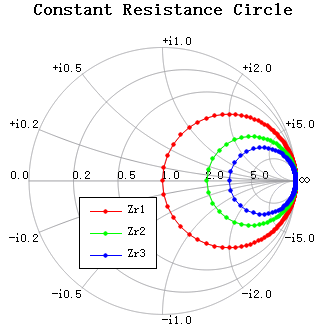 |
Smith chart |
| Image | 2D planar chart | 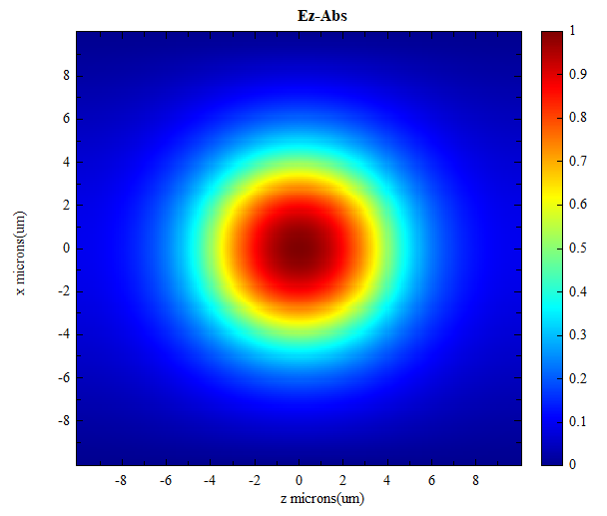 Take logarithm: Take logarithm: 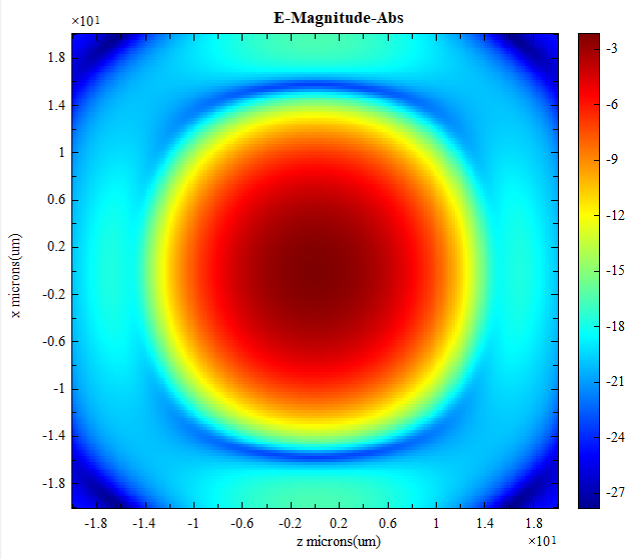 Add transverse vector: Add transverse vector: 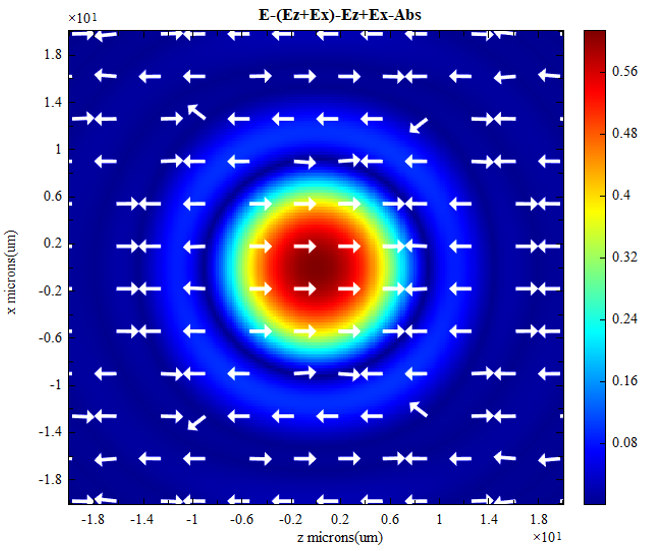 |
2D plot |
| Surf | 3D spatial surface chart | 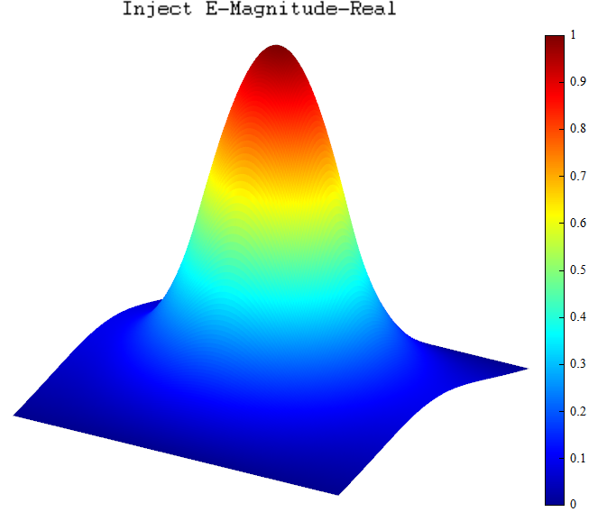 Take logarithm: Take logarithm: 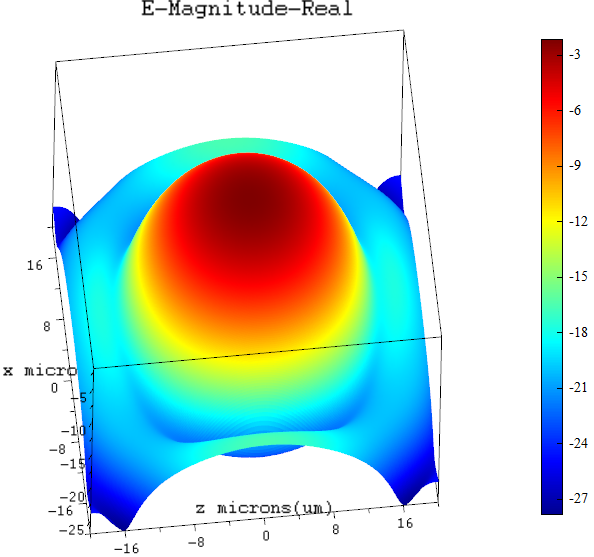 Add mesh: Add mesh: 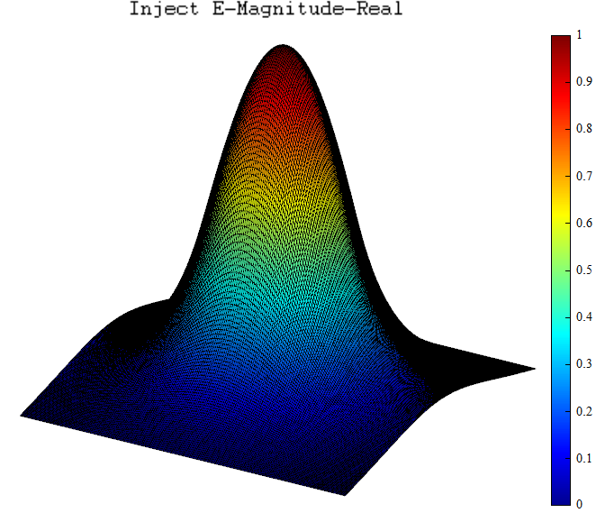 Radiation: Radiation: 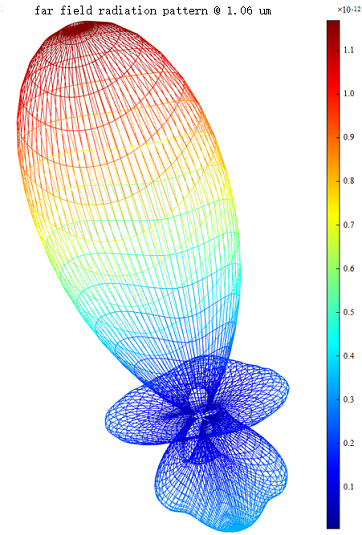 |
3D plot |
| Mesh | 3D spatial mesh chart | 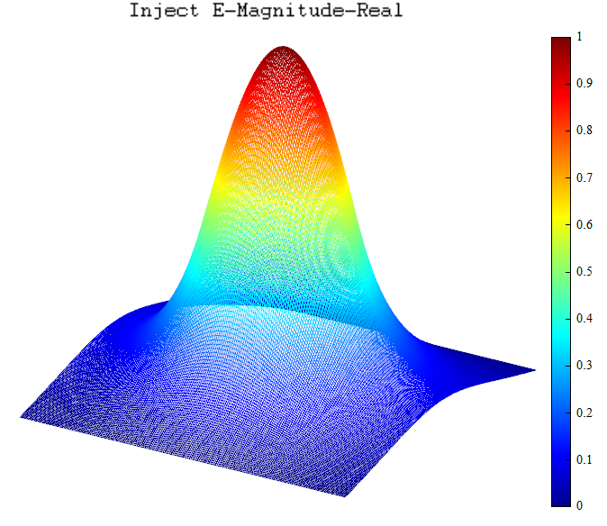 |
3D plot |
| Vector plot | 3D spatial vector graphic | 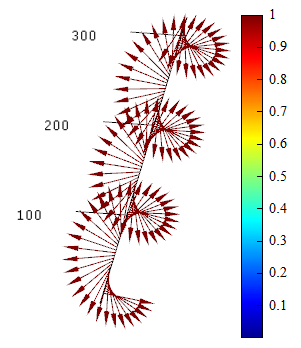 |
3D vector plot |